An article at PC World does a great job of summarizing the major developments in social networking space in 2007 and ponders over the prospects and uncertainties for 2008.
One insightful point mentioned in the article is how innovation at start-ups startles tech giants. Google, the great Web firm that one-upped Yahoo in claiming the search crown and hailed as the poster child of innovation was beaten at the social networking front. All the major internet firms such as Yahoo, Google and MS were done in by FaceBook which sort of perfected the concept of applications around social networks.
Social Networking is moving from the domain of an ‘nice add-on’ feature to a must-have even at the enterprise level. Various organizations are now waking up to the possibility that to attract the next generation of talent, it is essential to incorporate the flavor of social networking and connectivity within the enterprise.
While there were major salvos fired at FaceBook’s walled garden approach to social networking apps (which it did counter by licensing the F8 platform), it will be LinkedIn’s progress in the API space that will be really interesting. Being a site for business networking, it is one network that will really see a boost with professional networking going beyond just the website to the Web as such.
But another shift that can also be expected is the increased availability of affordable feature-rich mobile phones and compelling mobile applications. Apart from the enterprise user, the benefits of mobile applications have not really trickled down to the casual user. 2008 will hopefully be the year when mobile applications especially for social networking will really take off. Since Google has made several bold moves in the mobile space, expect a lot of innovation in this front.
Overall, its been a great year for Social Networking and for 2008 there’s a lot to anticipate.

 Working in tech support, I constantly run into a wide variety of users who seem to know very little about taking care of their Windows computers. This isn’t necessarily their fault, since most people simply don’t have the time or patience to dig beyond the surface-level workings of their computers. Ideally, users shouldn’t have to worry about the way their computer works, but that sort of blissful utopia is still several years away in my opinion.
Working in tech support, I constantly run into a wide variety of users who seem to know very little about taking care of their Windows computers. This isn’t necessarily their fault, since most people simply don’t have the time or patience to dig beyond the surface-level workings of their computers. Ideally, users shouldn’t have to worry about the way their computer works, but that sort of blissful utopia is still several years away in my opinion.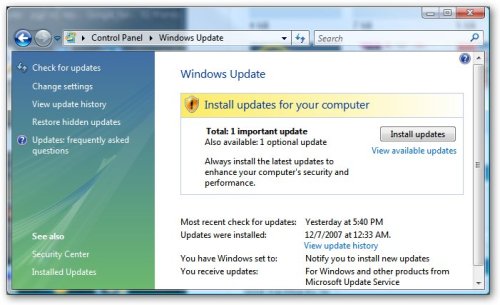

 Back in 2005 Qiu Chengwei, a 41 years-old Shanghai resident, stabbed fellow gamer Zhu Caoyuan repeatedly in the chest, causing his death. The reason? Zhu sold the “dragon sabre,” a weapon that they won jointly in the MMORPG (Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Game).
Back in 2005 Qiu Chengwei, a 41 years-old Shanghai resident, stabbed fellow gamer Zhu Caoyuan repeatedly in the chest, causing his death. The reason? Zhu sold the “dragon sabre,” a weapon that they won jointly in the MMORPG (Massively Multiplayer Online Role Playing Game). Earlier this year four Brazilian men, with ages between 19 and 28, developed a plan to steal the game password of a GunBound (an online multiplayer game) top player. The objective was to sell the game account on the Internet for $8,000.
Earlier this year four Brazilian men, with ages between 19 and 28, developed a plan to steal the game password of a GunBound (an online multiplayer game) top player. The objective was to sell the game account on the Internet for $8,000. Back in 2005 a Chinese girl nicknamed “Snowly” died of exhaustion after playing the MMORPG World of Warcraft for three days in a row. She was preparing to kill the Black Dragon Prince, other players explained, hence why she had no time to rest between the game sessions.
Back in 2005 a Chinese girl nicknamed “Snowly” died of exhaustion after playing the MMORPG World of Warcraft for three days in a row. She was preparing to kill the Black Dragon Prince, other players explained, hence why she had no time to rest between the game sessions. A couple of weeks ago a seventeen year-old boy stole almost $6000 worth of virtual furniture in the online game Habbo Hotel. Habbo is a virtual world where people can create houses and other scenarios, but the items need to be purchased with real money.
A couple of weeks ago a seventeen year-old boy stole almost $6000 worth of virtual furniture in the online game Habbo Hotel. Habbo is a virtual world where people can create houses and other scenarios, but the items need to be purchased with real money. The details about the case were not revealed, but two Belgian newspapers reported early this year that the Belgian Police would setup an in-game patrol unit to investigate virtual rape incidents.
The details about the case were not revealed, but two Belgian newspapers reported early this year that the Belgian Police would setup an in-game patrol unit to investigate virtual rape incidents. In the middle of 2005 Blizzard introduced a new area to its popular MMORPG, World of Warcraft. The boss of the area was able to cast a spell called Corrupted Blood, which was supposed to infect and cause damage to all the players nearby.
In the middle of 2005 Blizzard introduced a new area to its popular MMORPG, World of Warcraft. The boss of the area was able to cast a spell called Corrupted Blood, which was supposed to infect and cause damage to all the players nearby.