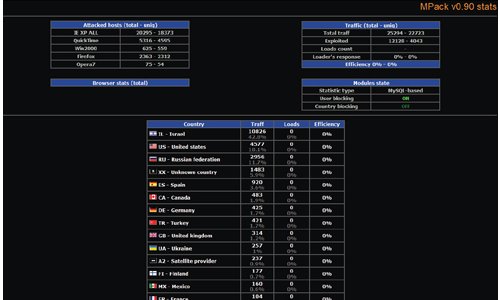
If you ended up wasting too much time with the previous two games that we covered (Helicopter and Desktop Tower Defense), this one might be the solution. The Last Stand is a cool game don’t get me wrong, and it is very graphically appealing for a flash game, but it is not that challenging.

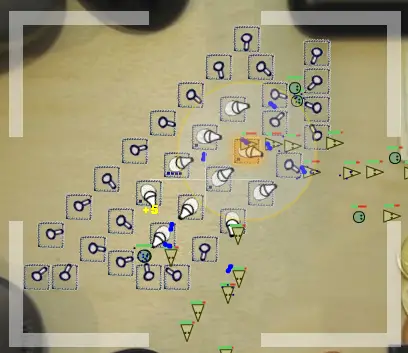
As you can see from the image above the game is about killing zombies. There is a minimum of strategy involved as you need to allocate your day time between finding survivors, weapons, and repairing the barriers that protects you. Once you get the M-40 weapon, though, the game is over.